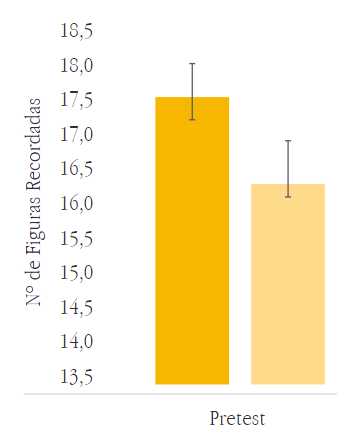
Array
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18270/chps..v17i2.2226Palabras clave:
Café, cafeína, cogniciónDescargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Adan, A., Prat, G., Fabbri, M., Sanchez-Turet, M. (2008). Early effects of caffeinated and decaffeinated coffee on subjective state, and gender differences. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 32, 1698–1703
Adan, A., & Serra,R. & Grabulosa, J. M. (2010). Effects of caffeine and glucose, alone and combined, on cognitive performance. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 25(4), 310-317.
Arab, L., Biggs, ML., O'Meara, ES., Longstreth, WT., Crane, PK., & Fitzpatrick, AL. (2011). Gender differences in tea, coffee, and cognitive decline in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study. J Alzheimers Dis.; 27(3):553-66. 29.
Aue, W.R., Arruda, J.E., Kass, S.J., Stanny, C.J. (2009). Cyclic variations in sustained human performance. Brain and Cognition, 71, 336-344.
Borota, D., et al. (2014). Post-study caffeine administration enhances memory consolidation in humans. Nat Neurosci. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nn.3623.
Brice, C.F.,& Smith, A.P. (2002). Effects of caffeine on mood and performance: a study of realistic consumption. Psychopharmacology, 164, 188-192.
Cappelletti, S., Daria, P., Sani, G., & Aromatario, M. (2015). Caffeine: Cognitive and Physical Performance Enhancer or Psychoactive Drug? Current Neuropharmacology, 13(1), 71–88. http://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X13666141210215655
Chamberlain, S.R., Muller, U., Robbins, TW., Sahakian, B.J. (2006). Neuropharmacological modulation of cognition. Current opinion neurology, 19, 607-612.
Chaytor, N., Schmitter-Edgecombe, M., & Burr, R. (2006). Improving the ecological validity of executive functioning assessment. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology , 21 , 217 – 227
Collette, F., Van der Linden, M. (2002). Brain imaging of the central executive component of working memory. Neuroscience Biobehavioral Review 26, 105-125.
Corley, J., Jia, X., Kyle, J., Gow, A., Brett, C., Starr, J., et al. (2010). Caffeine consumption and cognitive function at age 70: the Lothian Birth Cohort 1936 study. Psychosom Med. 72,2, 206-14.
Cunha, R. A. (2008). Cafeína, receptores de adenosina, memoria y enfermedad de Alzheimer. Medicina clínica, 131,20, 790-795.
De la Peña, C., Fernández-Medina, J. M., Parra-Bolaños, N., & Martínez-Restrepo, Ó. A. (2016). Estudio neuropsicológico en pacientes parkinsonianos: efectos de la estimulación cerebral profunda. Revista de Neurología, 62,4, 152-156.
Dodd, F. L., Kennedy, D. O., Riby L. M., & Haskell-Ramsay C. F. (2015). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effects of caffeine and L-theanine both alone and in combination on cerebral blood flow, cognition and mood. Psychopharmacology (2015) 232:2563–2576 DOI 10.1007/s00213-015-3895-0
Foxe, J.J., Morie, K.P., Laud, P.J., Rowson, M.J., Bruin, E.A., Kelly, S.P. (2012). Assessing the effects of caffeine and theanine on the maintenance of vigilance during a sustained attention task. Neuropharmacology, 62, 2320-2327.
Franco, R. (2009). Café y salud mental. Atención primaria, 41(10), 578-581.
Haskell, C.F., Kennedy, D.O., Milne, A.L., Wesnes, K.A., Scholey, A.B. (2008). The effects of L-theanine, caffeine and their combination on cognition and mood. Biological Psychology, 77, 113-122.
James, J. E. (2014). Caffeine and cognitive performance: persistent methodological challenges in caffeine research. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 124, 117-122.
Jurado, M. B., & Rosselli, M. (2007). The elusive nature of executive functions: A review of our current understanding. Neuropsychology Review, 17(3), 213-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11065-007-9040-z
Koppelstaetter, F., Poeppel, T. D., Siedentopf, C. M., Ischebeck, A., Kolbitsch, C., Mottaghy, F. M., & Krause, B. J. (2010). Caffeine and cognition in functional magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 20(S1), 71-84.
Koppelstaetter, F., . Poeppel, T.D., Siedentopf, C.M., Ischebeck, A., Verius, M., Haala, I., Mottaghy, F.M., Rhomberg, P., Golaszewski, S., Gotwald, T., Lorenz, I.H., Kolbitsch, C., Felber, S., Krause, B.J (2008). Does caffeine modulate verbal working memory processes? An fMRI study. Neuroimage. 1, 39,1, 492-9.
Lamina, S., & Musa, D. (2009). Ergogenic effect of varied doses of coffee-caffeine on maximal aerobic power of young African subjects. African Health Sciences, 9,4, 270–274.
Liang, N., & Kitts, D. D. (2014). Antioxidant property of coffee components: assessment of methods that define mechanisms of action. Molecules, 19,11, 19180-19208.
Liversedge, S. P., & Findlay, J. M. (2000). Saccadic eye movements and cognition. Trends in cognitive sciences, 4,1, 6-14.
Naidu, MM., Sulochanamma, G., Sampathu, SR., & Srinivas P. (2008). Studies on extraction and antioxidant potential of green coffee. Food Chemistry, 107, 377-84.
Nehlig A. (2010). Is caffeine a cognitive enhancer? Journal Alzheimers Dissease, 20 Suppl 1:S85-94. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-091315.
Rogers, P.J., Heatherley, S.V., Mullings, E.L., Smith, J.E. (2013). Faster but not smarter: effects of caffeine and caffeine withdrawal on alertness and performance. Psychopharmacology, 226,2, 229-40. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2889-4.
Sanchez-Cubillo, I., Perianez, J. A., Adrover-Roig, D., Rodriguez-Sanchez, J. M., Rios-Lago, M., Tirapu, J. E. E. A., & Barcelo, F. (2009). Construct validity of the Trail Making Test: role of task-switching, working memory, inhibition/interference control, and visuomotor abilities. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 15,3, 438.
Santacruz, M.P., Rodriguez, C.A. y Jimenez, M.L. (2007). Efectos de la cafeína en algunos aspectos de la salud y de la cognición. Revista Colombiana de Rehabilitación, 6, 73-90
Stuss, D. T., & Alexander, M. P. (2000). Executive functions and the frontal lobes: A conceptual view. Psychological Research, 63(3-4), 289-98. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004269900007
Tucha, O., Walitza, ., Mecklinger, L., Stasik, D., Sontag, T.A., Lange, K.W. (2006).The effect of caffeine on handwriting movements in skilled writers. Hum Move Sci 25, 523–535
Van Duinen, H., Lorist, M.M., & Zijdewind, I. (2005.) The effect of caffeine on cognitive task performance and motor fatigue. Psychopharmacology, 180, 539-547
Vanderveen, J. E., Armstrong, L. E., Butterfield, G. E., Chenoweth, W. L., Dwyer, J. T., Fernstrom, J. D., & Sternberg, E. M. (2001). Caffeine for the sustainment of mental task performance: formulations for military operations. National Academy, Washington, DC